More and more people are looking for ways to improve their health and make a positive contribution to the environment at the same time. According to a survey by the Federal Association of the German Food Trade (BVLH), one in ten people now eat a vegetarian or vegan diet. A plant-based diet is therefore becoming increasingly popular. But what are the real health benefits compared to animal protein and are there any potential disadvantages? This article takes a critical look at the pros and cons of a plant-based diet and sheds light on frequently asked questions.
Is plant protein just as good as animal protein?
The debate about the quality of plant and animal protein is complex. However, scientific research shows that plant-based protein can be an excellent source of essential amino acids, which are vital for the body. Legumes, nuts and whole grains not only provide protein, but also a wealth of vitamins, minerals and fibre, that are crucial for a balanced diet.
What has always been doubted is whether you can get “complete” protein from a plant-based diet. Complete proteins are those, which contain all nine essential amino acids, that the body cannot produce on its own and must therefore obtain from food. Some vegan proteins do not have all the essential amino acids, which promotes the belief that it is necessary to carefully balance the diet. A typical example of this is the combination of rice and beans, which are supposed to complement each other in the provision of amino acids.
However, experts are increasingly of the opinion that it may not be necessary to combine certain plant foods for their amino acids. A balanced plant-based diet most likely provides sufficient amounts of all 20 amino acids, both essential and non-essential. A study conducted in 2019 on people with vegan and vegetarian diets even found that they consume more than enough protein and amino acids. The concept of an amino acid deficiency therefore appears to be significantly overrated. (1)

However, there is one nutrient for which plant sources cannot compete with animal sources: Vitamin B12. This vitamin is essential for proper brain function and the formation of red blood cells. If you have opted for a purely vegan diet, it is probably advisable to take this vitamin via supplements.
Can plant-based protein have disadvantages?
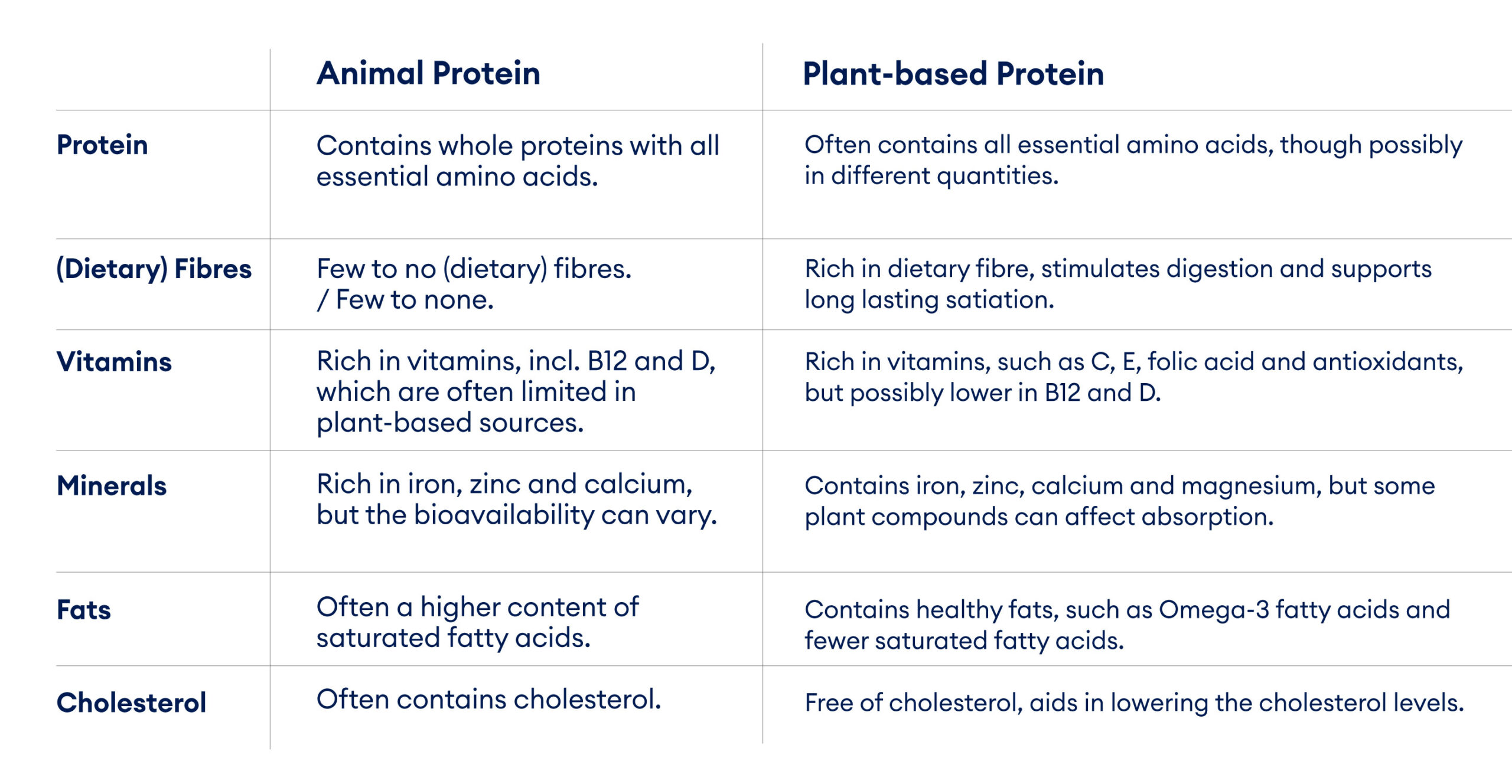
Choosing plant-based proteins over animal proteins is likely to have positive health benefits. Studies have linked a plant-based diet to positive weight management benefits, a lower risk of type 2 diabetes and even increased life expectancy. (2) However, there are pros and cons on both sides, which we have listed further in this table:
The environmental benefits of plant protein
The ecological footprint of plant-based protein is considerably smaller than that of animal protein. The production of plant-based foods requires fewer resources, such as water and land, and produces fewer greenhouse gases. By switching to plant-based protein, we can therefore not only protect our health, but also the environment:
- Reduction of the ecological footprint: Animal husbandry is responsible for a significant proportion of greenhouse gas emissions. Study results show that a vegan diet produces on average 75% fewer climate-damaging emissions. By avoiding animal products, each individual can reduce their ecological footprint and actively contribute to environmental protection. (3)
- Saving water: The production of plant-based foods generally requires less water than that of animal products. For example, around 1,000 litres of water are needed to produce 1 kg of grain, while 4 to 5 times as much water is needed to produce 1 kg of chicken and more than 10 times as much to produce 1 kg of beef. (4) Switching to a plant-based diet therefore also helps to save water.
- Preserving biodiversity: The massive use of land for livestock farming contributes to the destruction of habitats. A plant-based diet supports the preservation of biodiversity by up to 66% by reducing the pressure on natural ecosystems. (5)
5 clever tips to consume more plant-based protein
1. Start the day with plant-based protein power
The morning is the best time to eat a large portion of protein and supply your body with amino acids after an overnight fast. Start your day with a protein boost by adding plant-based protein sources such as nuts, seeds or oatmeal to your breakfast. This can be as simple as adding a handful of almonds to your muesli or chia seeds to your yoghurt. Today, vegan multi-component proteins also make it easy to consume high-quality plant-based protein.

2. Bring colours to the plate
Create a colourful palette on your plate by incorporating different vegetables into your meals. The more colourful, the better! This not only ensures a rich supply of nutrients, but also adds variety and flavour to your diet.
3. Snack-Attack with roasted chickpeas
Swap conventional snacks for plant-based protein sources. Instead of crisps, try roasted chickpeas or hummus with vegetable sticks. These little power packs contain around 15 grams of protein per cup. Bonus: they are crispy, delicious and perfect for on the go! Small changes in your snacking habits can make big differences in the long term.
4. Combine without over-analysing
Remember that it is not important to analyse every single amino acid profile. By combining different plant foods throughout the day, you automatically get a wide range of amino acids. Variety is the key here. Treat yourself and have fun discovering new plant-based options!
A plant-based diet has a multitude of health benefits and contributes to the sustainability of our planet. By making conscious choices and eating a balanced diet, we can not only promote our own health, but also have a positive impact on the environment.
Frequently asked questions about plant-based protein
There are numerous sources of sufficient protein in a purely plant-based diet. Plant sources such as pulses, nuts, seeds and wholemeal products are rich in protein. A varied diet ensures that all the necessary amino acids are covered.
With careful planning, a plant-based diet provides all the necessary nutrients. It is important to ensure a balanced selection of foods and to consider dietary supplements if necessary.
It is particularly important for athletes to consider individual protein needs and ensure that they are getting adequate amounts of high-quality protein from a variety of plant sources. A varied and balanced diet, combined with supplemental protein powders if necessary, is part of an effective nutrition plan for athletes.
(1) Nutrients: Dietary Protein and Amino Acids in Vegetarian Diets—A Review
(2) Nature: The effects of plant-based diets on the body and the brain: a systematic review
(3) Science Direct: A comprehensive review on carbon footprint of regular diet and ways to improving lowered emissions
(4) ResearchGate: Water and Agriculture: Harvesting water before harvesting the crop
(5) The Guardian: Vegan diet massively cuts environmental damage, study shows
